Sjogren’s Syndrome
 Sjogren’s syndrome is a condition causing chronic systemic inflammation in the exocrine glands of the body such as salivary glands like Parotid gland, tear secreting glands like Lacrimal gland. Sjogren’s can occur in itself as an autoimmune condition and is termed Primary Sjogren's or as a part of a disease spectrum with other conditions such as Rheumatoid arthritis and is termed secondary Sjogren’s.
Sjogren’s syndrome is a condition causing chronic systemic inflammation in the exocrine glands of the body such as salivary glands like Parotid gland, tear secreting glands like Lacrimal gland. Sjogren’s can occur in itself as an autoimmune condition and is termed Primary Sjogren's or as a part of a disease spectrum with other conditions such as Rheumatoid arthritis and is termed secondary Sjogren’s.
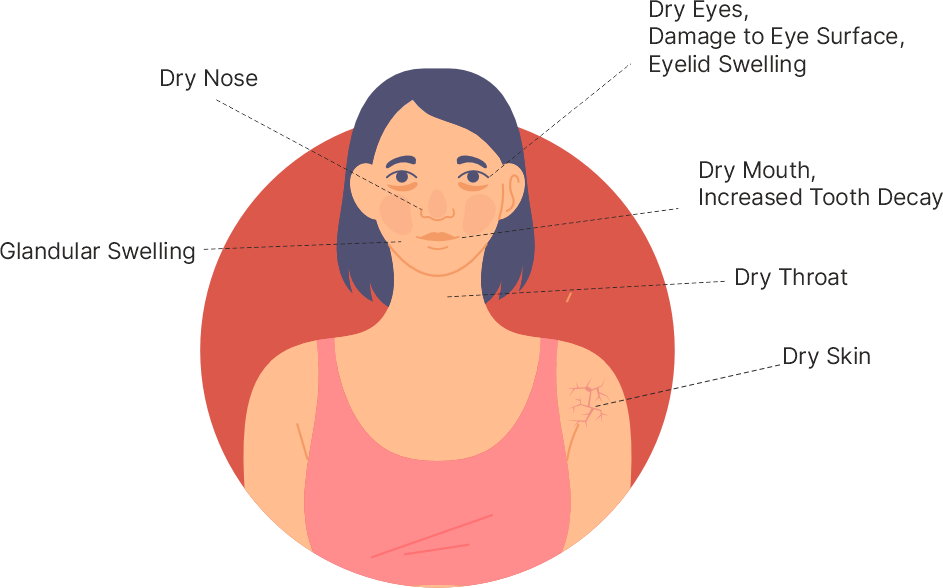
In Sjogren's the immune system causes chronic inflammation of the exocrine glands which get damaged. Exocrine glands are responsible for the production of sweat, tears, saliva and digestive enzymes in the body. In Sjogren’s there is reduced production of these substances causing dryness especially of the eyes and the mouth. Similarly, digestion is also affected due to reduced digestive enzyme secretions.
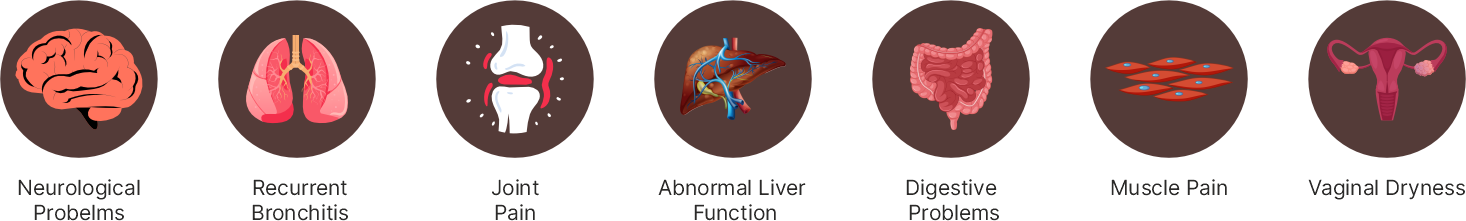
This condition is seen in women and women are more affected than men especially after 50 years. In patients with Rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's can occur earlier as a part of the disease spectrum. Common symptoms include dry eyes and dry mouth which are together termed as SICCA syndrome. Joint pains and fatigue are common.
Sjogren's syndrome can also lead to complication when not treated. Common complications are low blood cell counts including white and red blood cells. Nerves can be affected. Due to decreased secretions which are protective, frequent eye and teeth infections are common. Similarly due to low secretions, infections in the lungs and digestive system occur. Diagnosis requires detailed history and examination as the symptoms can be found in other conditions. Blood testing for cell counts and presence of autoantibodies are important for diagnosis.
